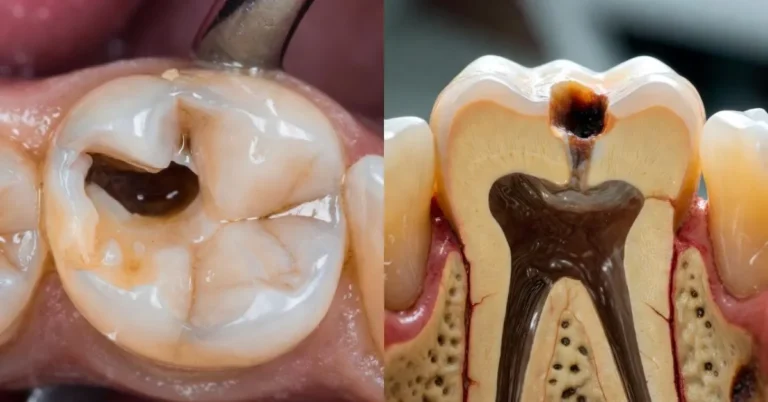
The Promise Of Tooth Enamel Regeneration Comes In A Gel
In the ever-evolving landscape of dental care, a groundbreaking development is adding to tooth restoration’s possibilities, offering new hope for those grappling with decaying teeth. The traditional approach to treating tooth decay has often involved dental fillings or crowns, but a recent breakthrough has opened the door to a more revolutionary solution – tooth enamel…