Bringing a new product to market is rife with uncertainty. How can manufacturers truly know if their latest innovation will resonate with consumers once it hits shelves? After investing immense resources into development, the last thing brands want is a flop. This dilemma leaves companies facing a critical question: should they rely on traditional controlled testing or real-world in-home usage testing (IHUT) to gain the most accurate pre-launch consumer insights?
This article explores the nuances between these prominent testing methodologies, comparing their strengths and weaknesses. By examining key factors such as cost, speed, flexibility, and contextual accuracy, we aim to determine which approach provides superior feedback, minimizing the risks of product failure. Ultimately, real-world testing emerges as the gold standard for anticipating how offerings will fare with end users in practice rather than theory.
Demystifying In-Home Usage Testing
In-home usage testing (IHUT) ships new product samples directly to carefully selected consumers to utilize within their own homes and daily environments. While convenient for testers, IHUT introduces variability that lab testing avoids.
While IHUT offers invaluable real-world data, it trades the reliability of controlled conditions for organic but variable testing environments. This emphasizes the need for comprehensive IHUT research to capture authentic insights into how products perform in real consumer settings.
Advantages of IHUT:
- Furnishes authentic real-world feedback based on actual in-context product usage rather than theoretical responses.
- A cost-effective way to preliminarily test product iterations before mass production. IHUT costs approximately 70% less than traditional lab testing.
- Participants can conveniently access and sample products in natural settings and leisurely timeframes within their homes.
- Follow-up surveys collect comprehensive qualitative insights on real-use scenarios.
Disadvantages of IHUT:
- Can be time-consuming and require a large sample size of at least 100 participants for statistical significance.
- Subjective, highly variable feedback. Product reactions and preferences are influenced by individuals’ unique needs.
- Results are shaped by user demographics, lifestyles, and predilections. Feedback inherently represents certain consumer subsets rather than the entire target audience.
Defining Traditional Lab Testing
Traditional product testing refers to the process of methodically evaluating new products within tightly controlled laboratory environments. The core objectives are to identify any defects in the product early on and verify overall quality before full-scale market launch.
As one industry source outlined, traditional testing works optimally when product requirements and specifications are delineated upfront. This is because once testing has commenced, implementing modifications or changes becomes exponentially more difficult.
Advantages of Traditional Testing:
- Helps expose the maximum number of flaws and defects. According to one scientific study, traditional lab testing successfully uncovers up to 75% of product issues.
- Ensures a higher quality, more rigorously-tested product. Contained testing enables preventing bug-ridden or deficient products from ever being released to the market.
Disadvantages of Traditional Testing:
- Time-consuming and taxing process. In some cases, the full traditional testing process can stretch across many months from start to finish. This delays the speed to market.
- Minimal flexibility to make changes once testing begins. Any modifications or alterations after testing has started can greatly prolong overall timelines.
- Focuses heavily on documentation over reusability. Traditional testing methods tend to prioritize thorough documentation of all processes over developing reusable testing components.
- Works best when requirements are precisely defined upfront. Since changes become difficult post-commencement, traditional testing requires defined specifications.
While traditional controlled testing enables robust quality assurance, it trades speed, flexibility, and real-world context for rigorous isolated testing environments.
Head-to-Head Comparison
| Factor | Traditional Testing | IHUT |
| Cost | More expensive | Cost-effective |
| Time | Quicker completion | Can take longer |
| Context | Controlled environment | Real-world usage |
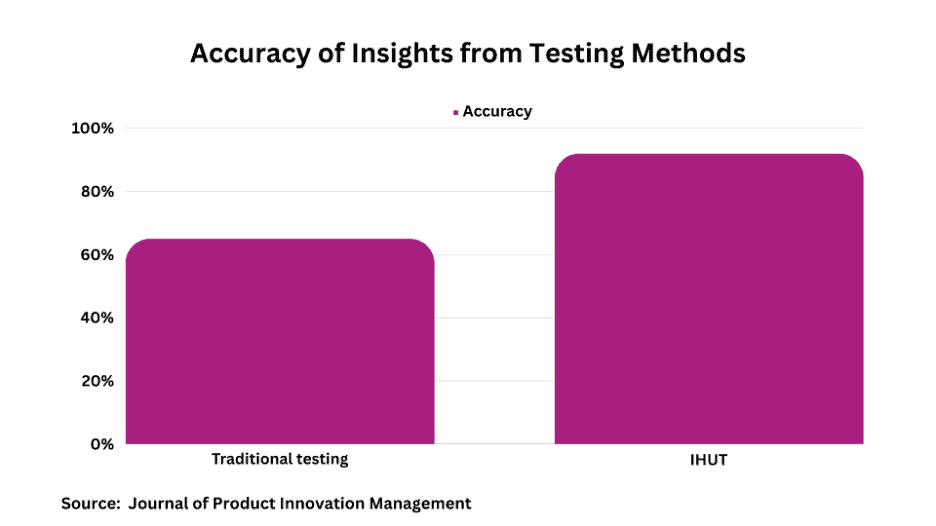
| Accuracy | Less accurate | More accurate |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | More flexible |
Crowning the Superior Methodology
While both techniques have merits, IHUT emerges as the foremost product testing methodology for most consumer products, based on available research. Producers gain invaluable data on how target users interact with their offerings in everyday environments. This catalyzes refinements that optimize appeal, usability, and customer adoption.
Despite extended timelines, the unmatched real-world accuracy and actionability of discoveries garnered make IHUT the gold standard. For ensuring offerings resonate rather than repel, there is simply no alternative for directly observing usage in native habitats.
The verdict? IHUT reigns supreme.
Optimizing Traditional and IHUT Approaches
While both traditional and IHUT testing offers valuable insights, each technique can be enhanced further by applying best practices:
Enhancing Traditional Testing
To get the most out of traditional lab testing, brands should incorporate diverse use cases into testing scenarios to cover a wider range of potential real-world user actions. Allowing some flexibility for iterative changes even after testing has started can also improve the final product.
Documentation should be limited only to essential technical and functional specifications to reduce administrative overhead. Finally, increasing collaboration between testers and teams allows discoveries to be shared in real time so efficiencies can be maximized.
Boosting IHUT Impact
For optimal IHUT testing, brands must carefully ensure participant demographics closely match the target purchaser profile. Detailed instructions and hands-on tech support should be provided to participants to guide product usage properly. Probing questions in post-study surveys helps unpack the contextual reasons behind specific behaviors or feedback.
Having participants maintain usage diaries provides richer qualitative insights into the end-user experience. With thoughtful implementation, IHUT produces multidimensional feedback no lab could ever replicate.
The Future of Product Testing
As technology progresses, product testing continues evolving through advances like:
- Remote testing allows consumers to assess smart products virtually.
- VR simulating product experiences before physical prototyping.
- AI predicts usage patterns to optimize the design.
- Crowdsourced testing generates wide user feedback.
While new techniques arise, IHUT and traditional testing will remain the go-to approaches for their proven utility. Rather than replacing established methods, emerging testing innovations promise to complement current best practices.
The Key Takeaway? Prioritize Real-World Insights
While both traditional controlled testing and IHUT deliver valuable product feedback, real-life home usage ultimately provides the most accurate window into consumer behavior. For optimal results, brands should adopt IHUT as the primary testing methodology and supplement it with traditional techniques as needed. There is simply no better test arena than the messy, unpredictable, wonderfully real contexts of everyday users.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What’s the difference between IHUT and traditional testing?
IHUT sends new products directly to selected everyday consumers to test and provide feedback in their homes and real-life settings. In contrast, traditional testing evaluates products in tightly controlled laboratory environments.
- What are the advantages of IHUT?
The main benefits of IHUT are that it offers authentic, real-world insights into how average users genuinely interact with and respond to products in natural contexts, and it provides an affordable way to conduct preliminary testing before full production.
- What are the disadvantages of traditional testing?
Traditional testing can be prohibitively expensive and time-consuming while yielding less flexible, accurate, and real-world relevant data compared to IHUT since products are tested in artificial laboratory settings rather than in realistic user environments.